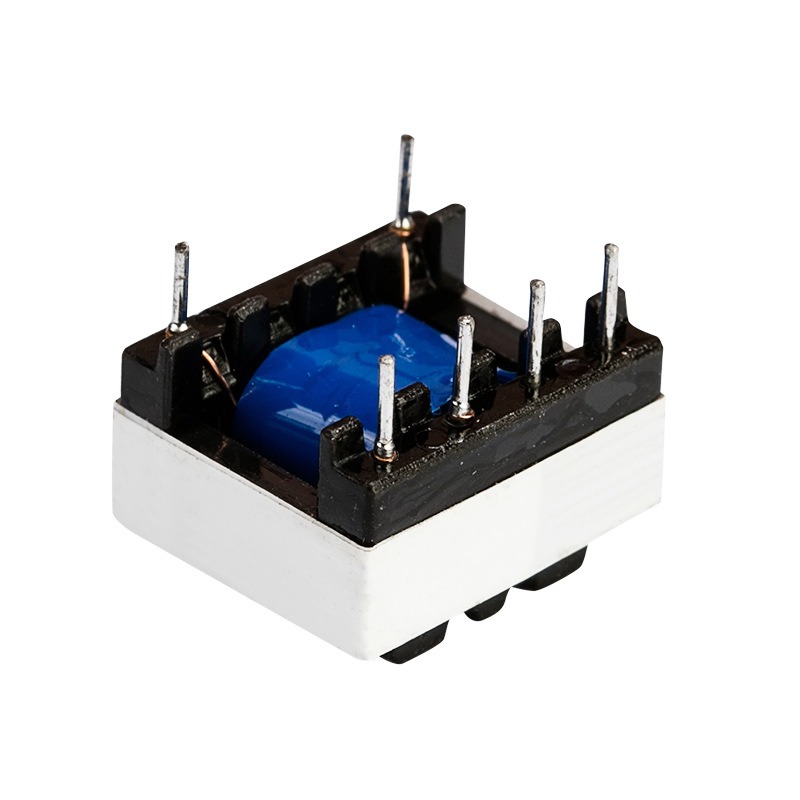

Custom Low Frequency Transformers for Reliable Power Conversion
Low frequency transformers are commonly used in industries such as industrial equipment, vending machines, and lighting systems, where efficient energy conversion is still essential. Compared to high frequency transformers, they offer a simpler solution while remaining equally effective.
At Shenzhen Kunyo Tech, we offer a variety of transformer sizes tailored to different power ranges. Our low frequency transformers are available for standard frequencies such as 50/60 Hz, 60 Hz, and 400 Hz.
We specialize in providing high-quality custom low frequency transformers, including:
EI-type transformers
Isolation transformers
Autotransformers
Toroidal transformers
Pin-type transformers
Audio transformers
BK control transformers
220V/110V voltage converters
You’re welcome to share your design requirements with us—we’re ready to develop a solution tailored to your application needs.
Audio transformers are engineered to function across a wide frequency range by designing their internal winding capacitance to resonate with inductance. This resonance extends the frequency response and allows for a more compact transformer core.
When installed between an amplifier and a speaker, audio transformers primarily provide electrical isolation. With no direct connection between primary and secondary windings—often configured with a 1:1 turns ratio—they isolate input and output circuits without changing voltage or current levels.
In addition to isolation, audio transformers serve a crucial role in impedance matching. Correct impedance matching minimizes signal loss and distortion, ensuring efficient power transfer between amplifiers and speakers.
They are especially effective for balancing amplifiers with loads that have differing input and output impedances, maximizing performance.
Many audio transformers feature multiple primary or secondary windings with taps, enabling various impedance options and gain or attenuation levels. This versatility supports precise impedance matching for a wide range of amplifier and speaker configurations.
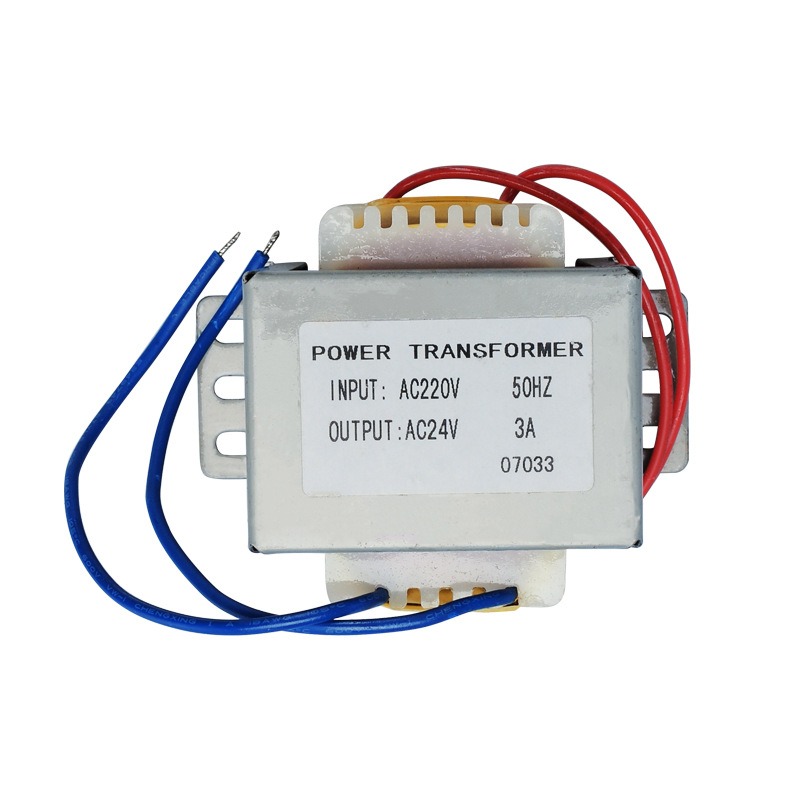

Iron Core: The iron core forms the central part of low-frequency transformers and is typically made from an iron-silicon alloy. Its primary function is to provide a low-reluctance magnetic path, minimizing energy loss during operation.
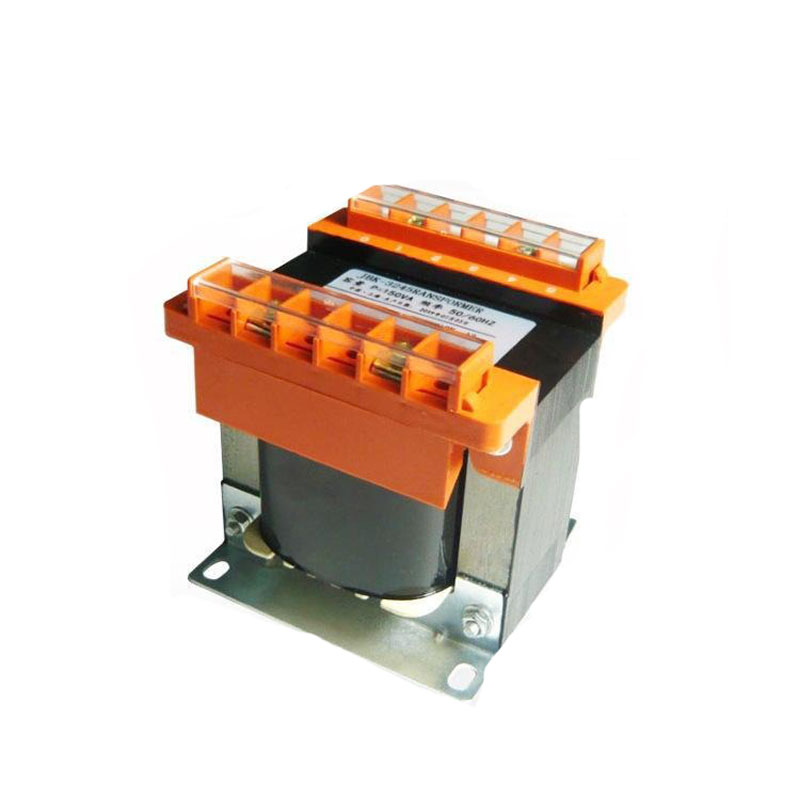

Winding: The winding is a coil of wire, consisting of primary and secondary windings. The primary winding connects to the input power source, while the secondary winding connects to the output load. These windings are magnetically linked through the iron core to facilitate energy transfer and conversion
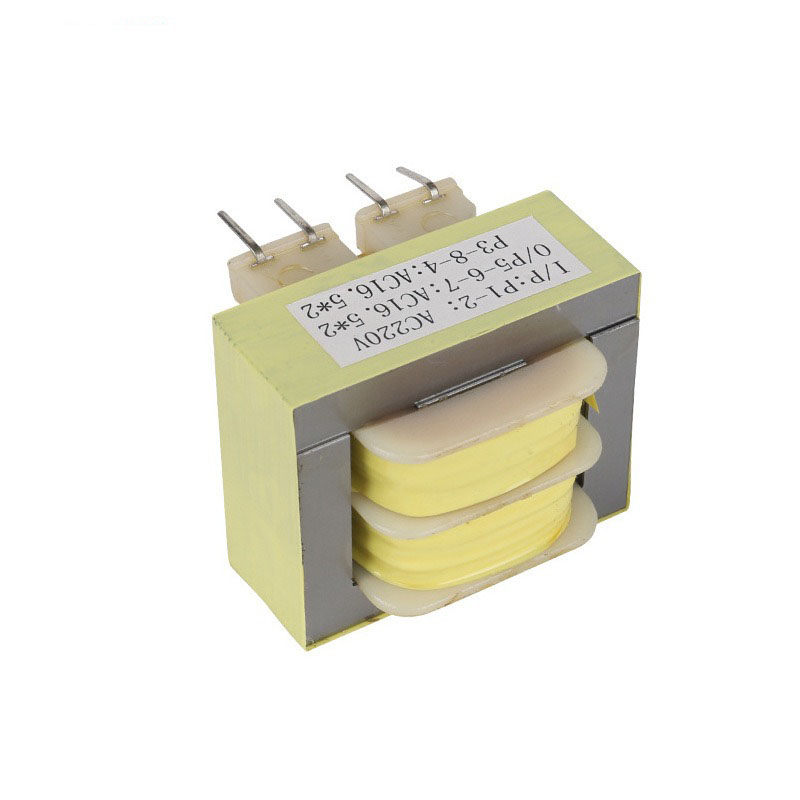

Case: The casing, typically made from insulating materials, encloses the entire transformer to protect the windings and iron core while reducing the risk of electric shock. It also assists in heat dissipation, helping to maintain the transformer’s temperature within safe operating limits.

Based on the assembly method, types include pin-type, drawer-type, and mother-and-child sleeve. By shape, they are categorized as I-shaped or W-shaped. Common materials used are nylon, polypropylene (PP), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and others.

Classified by color, the sheets come in white, black, and gray. By common material types, they include H50, H18, Z11, and others. In terms of thickness, typical options are 0.5mm and 0.35mm. Regarding shape, they are available in EI, UI, and ring configurations, among others.
Specifications such as temperature rating, voltage, current, and safety marks—for example, RH130-2, 250V, 2A, and the PSE mark—are typically printed on the product. Please ensure compliance with the molding requirements outlined in engineering specifications during use.

When selecting electronic wire for a low-frequency transformer, key factors to consider include the UL wire number, wire diameter, color, length, insulation type, and terminal fittings.
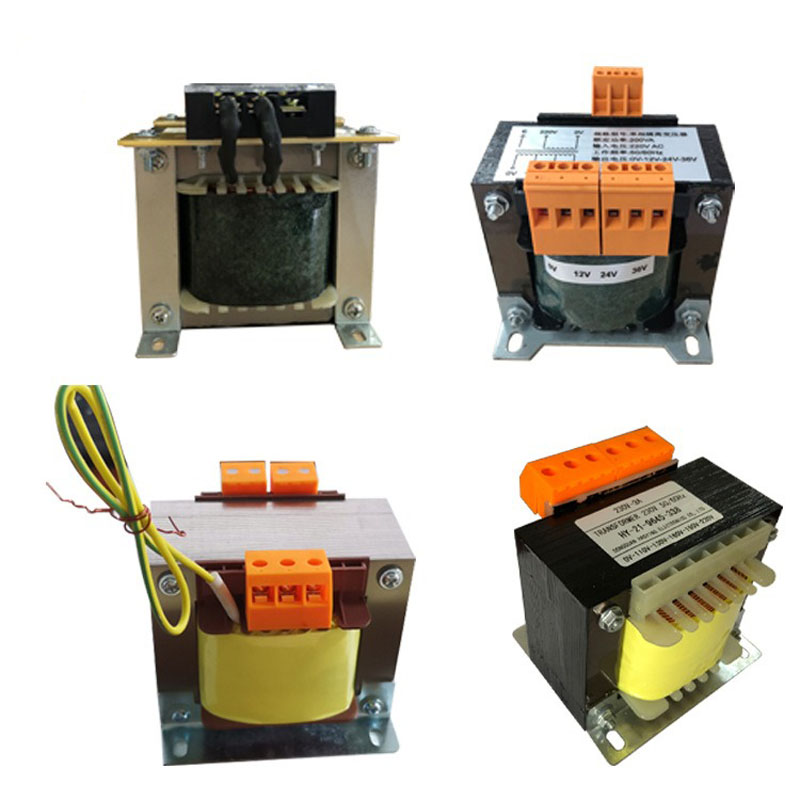

Kraft paper is available in both fireproof and non-fireproof types. For the iron bridge, options include horizontal and vertical orientations, round or square ears, and various electroplated materials.
The working principle of a low-frequency transformer is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction and the law of conservation of energy. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field that induces eddy currents in the transformer core. These eddy currents create a changing magnetic flux within the core, which then induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding, producing an output voltage.
The ratio of the transformer’s output voltage to its input voltage is known as the transformation ratio. This ratio can be adjusted by changing the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings. If the transformation ratio is less than 1, the transformer is a step-down transformer; if it is greater than 1, it is a step-up transformer.
Key performance parameters of low-frequency transformers include:
Rated Power: The maximum continuous power the transformer can deliver, typically expressed in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
Turns Ratio: The ratio of the number of turns in the secondary winding to the number of turns in the primary winding, which determines the ratio between input and output voltages.
Transformer Efficiency: The ratio of output power to input power, expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency indicates lower energy losses during operation.
Low-frequency transformers play a vital role in household appliances, widely used to ensure reliable power transmission through the principle of electromagnetic induction. They provide a stable electrical environment, supporting the safe and efficient operation of home devices.
As technology advances and consumer demands evolve, the application of low-frequency transformers in household appliances is expected to grow even further. Looking ahead, these transformers are poised to expand into more areas, enhancing convenience and improving the quality of everyday life.
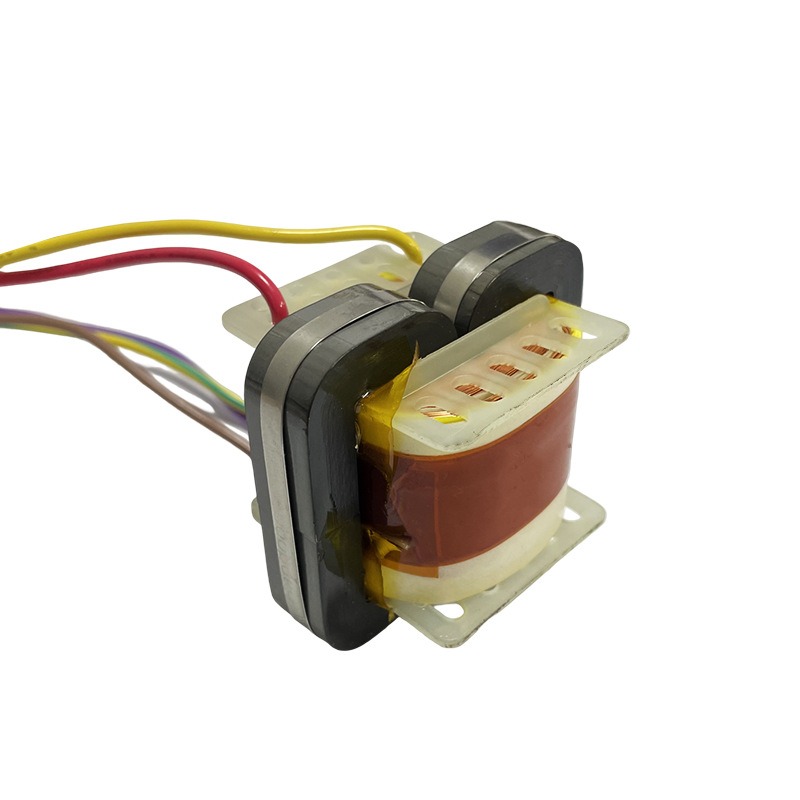
Low-frequency transformers play a crucial role in televisions. Modern TVs contain numerous sensitive electronic components that demand highly stable voltage for proper operation. A low-frequency transformer helps convert an unstable input power supply into a stable output voltage, creating a reliable power environment for the internal circuitry.
Without the support of a low-frequency transformer, voltage fluctuations could lead to issues such as blurry images, distorted sound, or even permanent damage to the TV’s internal components.
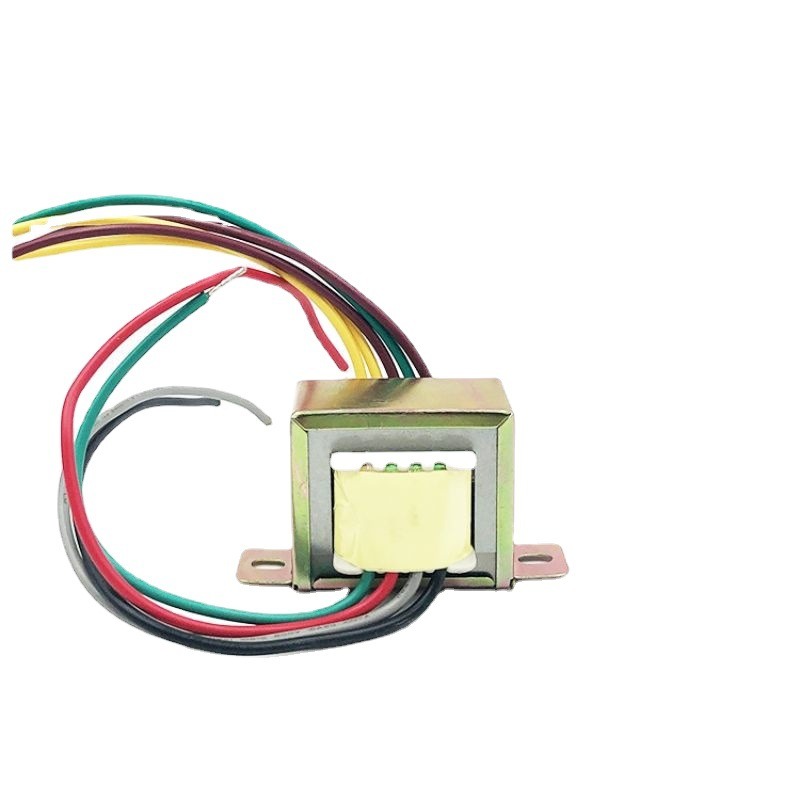
The low-frequency transformer also plays a vital role in the operation of a refrigerator. The compressor—often considered the heart of the refrigerator—requires a highly stable power supply for reliable startup and continuous operation. A low-frequency transformer ensures that the compressor receives a consistent voltage, which helps extend its lifespan and enhances the refrigerator’s cooling efficiency.
Without a low-frequency transformer, voltage instability may cause the compressor to start and stop frequently. This not only increases energy consumption but also reduces cooling performance and shortens the overall service life of the refrigerator.
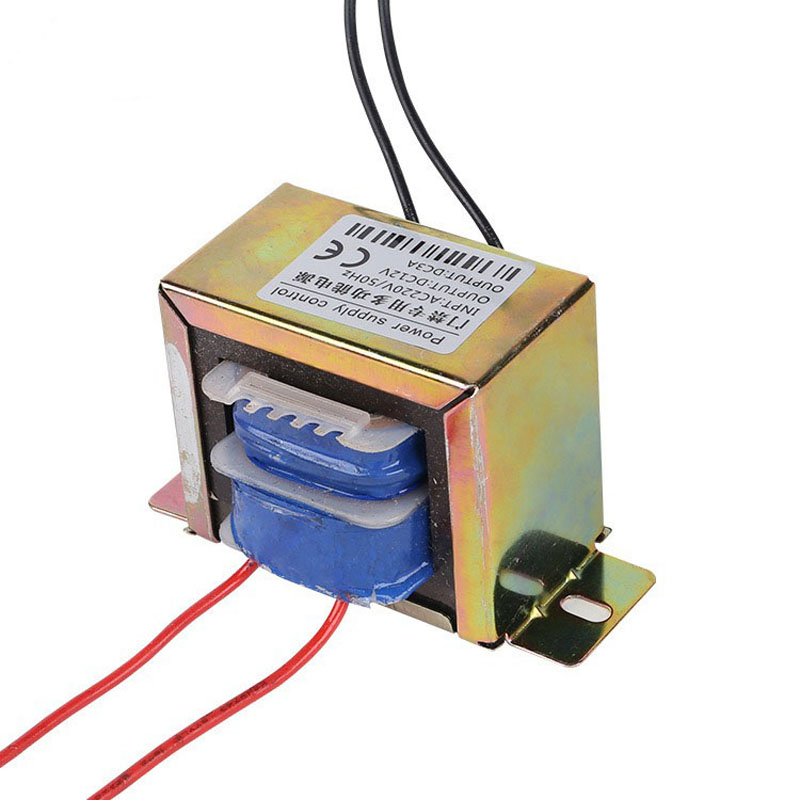
Air conditioners are essential household appliances in modern homes, and low-frequency transformers play a critical role in their operation. Inside an air conditioner, components such as control circuit boards and motors require a stable voltage supply to function effectively. Low-frequency transformers help maintain this voltage stability, enhancing both the performance and lifespan of the air conditioner.
Additionally, these transformers help reduce electromagnetic interference and radiation generated during operation, contributing to a safer environment by minimizing potential impacts on human health.

The electromagnetic oven, commonly known as an induction cooker, is a popular appliance in modern kitchens. It heats cookware using the principle of electromagnetic induction. Within the induction cooker, the low-frequency transformer plays a crucial role by converting standard 220V household AC power into low-frequency AC suitable for the cooker’s operation. This enables rapid and efficient heating performance.

In addition to the appliances mentioned earlier, low-frequency transformers are also widely used in other household devices such as washing machines, microwave ovens, and rice cookers. These appliances require a stable power supply during operation to ensure proper functioning of their internal circuits.
By utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction, low-frequency transformers deliver consistent electrical energy, helping to maintain reliable performance and extend the service life of these household appliances.
Established in 2013, Shenzhen Kunyo Technology is committed to designing and manufacturing custom magnetic components, including high-frequency transformers, low-frequency transformers, audio transformers, power transformers, and inductors.
Contact us right now to get more information, we will have people reply within 12 hours.
You can get a price of this model or send us any question to get any information you would like to know, we will reply to you soonest.